Difference between revisions of "Additional Information"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Port forwarding) |
(→Port forwarding) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
:: is broadcast and should only be used locally. | :: is broadcast and should only be used locally. | ||
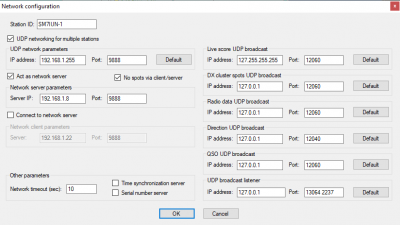
| − | '''Example configuration for server for networking over internet''' | + | |
| − | + | :: [[image:serverconfig.png|400px]] | |
| + | :: '''Example configuration for server for networking over internet''' | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
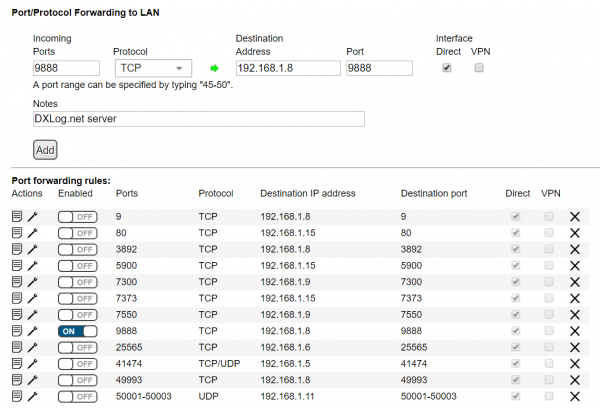
::[[image:portforwarding.png|600px]] | ::[[image:portforwarding.png|600px]] | ||
| − | + | ::'''Example of port forwarding UI in router''' | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
* All other PC in the multi-station set up should be set up as clients. | * All other PC in the multi-station set up should be set up as clients. | ||
:* Over the internet, "Server IP" is either the public IP address of the server's internet | :* Over the internet, "Server IP" is either the public IP address of the server's internet | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
:: over the internet does not have to enable UDP networking and ''should not'' enable a server. | :: over the internet does not have to enable UDP networking and ''should not'' enable a server. | ||
:* A client may connect via UDP if it is on the same LAN as the server ''or'' a "master client". | :* A client may connect via UDP if it is on the same LAN as the server ''or'' a "master client". | ||
| − | :: A "master client" is a client that connects to the server as | + | :: A "master client" is a client that connects to the server using the "connect as client" option in |
| − | + | :: the networking set up panel. A "master client" can act as a UDP gateway which means that if | |
| − | + | :: several computers on a LAN are part of the same multi station set up but the server is located | |
| − | + | :: elsewhere, only one computer in that LAN needs to connect as a client and the rest can use UDP. | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | |||
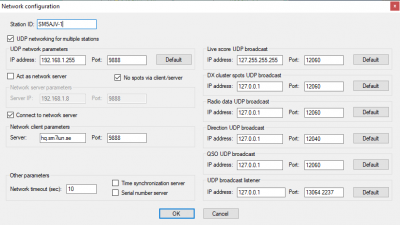
::[[image:clientconfig.png|400px]] | ::[[image:clientconfig.png|400px]] | ||
| − | + | ::'''Example configuration of client for networking over internet''' | |
| − | * Software interlock over internet | + | <br> |
| − | * | + | <br> |
| − | * Make sure <code>Options->Enable network</code> is checked | + | * Software interlock over internet is not reliable. On the other hand there is normally no need for it. |
| + | * In a multi-station setting it is recommended to enable <code>Options->Networking->Don't allow QSO logging if operator isn't logged</code> | ||
| + | * Make sure <code>Options->Enable network</code> is checked. | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 9 June 2019
Networking over internet
For particular events like when activating a special event callsign or running a HQ station in the IARU HF Championships, it is possible to network DXLog.net instances over the internet.
VLAN
The most secure way to do this is to rely on a VLAN (virtual LAN) software. There are several available such as:
LogMeIn Hamachi https://www.vpn.net/
FreeLan http://www.freelan.org/
Player.me https://player.me/
ZeroTier https://www.zerotier.com/
Port forwarding
If you are less worried about competitors or government agencies listening in on your contest data, it is possible to route the traffic directly over the internet using port forwarding at the server.
To do this, the following must be observed:
- Only one of the stations should be configured as the server.
- "Connect as client" should not be checked and "UDP network broadcast" should only be enabled if it is
- used to communicate with another client on the same LAN.
- The PC acting as server must have a fixed LAN IP address. This is done either by manually configuring the
- PC to use a fixed LAN IP address, or by setting up the router in the server's LAN to to always allocate
- the same IP address to it.
- The internet connection used by the server PC must either have a fixed public IP
- address or use dynamic DNS. Otherwise clients will not be able to reliable connect over the internet.
- The server's IP port (default 9888) must be forwarded to the internet by configuring the router
- connecting the server to internet. Only TCP traffic should be forwarded. DXLog.net UDP traffic
- is broadcast and should only be used locally.
- All other PC in the multi-station set up should be set up as clients.
- Over the internet, "Server IP" is either the public IP address of the server's internet
- connection (e.g. 5.150.248.52) or the dynamic DNS address (e.g. hq.sm7iun.se). Clients connecting
- over the internet does not have to enable UDP networking and should not enable a server.
- A client may connect via UDP if it is on the same LAN as the server or a "master client".
- A "master client" is a client that connects to the server using the "connect as client" option in
- the networking set up panel. A "master client" can act as a UDP gateway which means that if
- several computers on a LAN are part of the same multi station set up but the server is located
- elsewhere, only one computer in that LAN needs to connect as a client and the rest can use UDP.
- Software interlock over internet is not reliable. On the other hand there is normally no need for it.
- In a multi-station setting it is recommended to enable
Options->Networking->Don't allow QSO logging if operator isn't logged - Make sure
Options->Enable networkis checked.